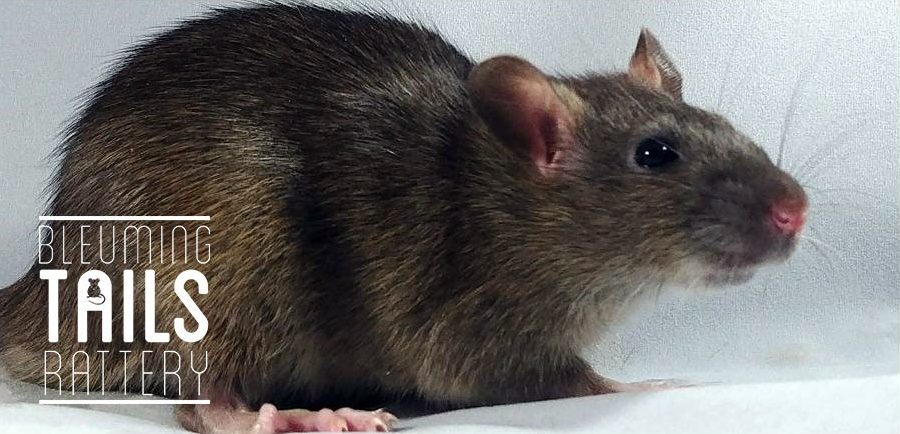
Black and Agouti
Agouti is the natural color of wild rats. Each individual hair shaft is banded with yellow, red and black pigment vs being a solid-colored shaft. The typical Agouti color is a rich chestnut with dark slate at the base of the hair. However, domestic Agouti rats tend to be much brighter in color which can be furthered when the animal carries red-eye dilute or pink-eye dilute.
Found on the A locus
Chromosome 3
Genetics
Agouti has two alleles “A” Agouti, and “a” non-Agouti or Black. Dominant “A” produces the banding of hair we know as Agouti. Recessive “a” produces solid colored hairs. When on an animal without any other recessive, Aa and AA will all produce an Agouti animal. aa indicates the animal is black. Unlike any other recessive, every single rat has an active A locus. This means that all rats, regardless of final coloration, are either Agouti-based or Black-based.
If bred, an Aa rat can pass on either the Agouti allele or the non-agouti allele. In an AA rat, only the Agouti allele can be passed on to offspring. In an aa rat, only the Black allele can be passed on to offspring.
AFRMA Standard: The color to be a rich chestnut with dark slate at the base of the hair. Coat is evenly ticked with black guard hairs. Belly color will be silver gray. Eye color is black.
NFRS Standard: To be a rich ruddy brown, evenly ticked with black guard hairs. Base fur dark grey to black. Belly fur to be silver grey. Foot colour to match top. Eyes black.
United Rat Community Standard: TBD
You may like:
Keeler (1942) found significant differences in behavior between agouti and black rats, but no clear, sharp division between the animals of different coat color.
Temperament
In a series of studies, scientists tested the theory that Agouti-colored rats were more difficult to tame than their Black counterparts. Of course, temperament is a complicated beast and many other factors go into the general tameness of an animal.
Keeler (1942): agouti and black rats
The rats: Keeler (1942) acquired Agouti and Black rats by crossing albino laboratory rats with wild Agouti rats. The offspring were all Agouti or Agouti berkshires. These hybrid offspring were then crossed together producing rats that were either agouti, black or albino with solid, berkshire or hooded patterns. These rats were not handled post-weaning, and were not allowed to be socialized by experimenters.
The tests: Keeler put these second-generation Agouti and Black rats through a variety of behavioral tests to study how docile they were.
The results: When the rats were picked up and gently held for the first time, the Agouti rats were noticeably more likely to display untame behaviors than the black rats. More Agouti rats bit (40% of Agouti rats vs. 10% of Black rats), squealed (68% vs. 37%), laid their ears back (45% vs. 10%) and urinated (51% vs. 7%) than their black counterparts. In addition, only 1% of agouti rats showed no reaction upon being picked up, compared to 30% of black rats.
More agouti rats than black rats responded to mild annoyance. When their noses were tickled lightly with a fine brush, 86% percent of agouti rats bit compared to only 20% of black rats. Agouti rats were also much more reactive; only 15% of agouti rats showed no reaction to the brush, compared to 73% of black rats.
The intensity of the responses varied between the two colors as well. The squeals of the agouti rats were often loud and prolonged, while those of black rats were short and soft and tended to decline into a protesting whine. The urination of the agouti rats was a strong spurt or stream; the urination of the black rats was a slow emission of one or a few drops. Agoutis defecated three to five boluses of feces; black rats frequently defecated only a single bolus. Lastly, agouti biting entailed a series of six or seven forceful bites delivered with “machine-gun rapidity,” while in the black rat the bite was often a single, weak nip.
The response to handling wasn’t the only difference. Agouti rats were more cautious than black rats in emergence tests. When the cage door was opened, agouti rats took an average of 84 seconds to come out, while black rats took only 57 seconds. After three minutes, 49% of the agouti rats had emerged, compared to 73% of black rats.
Keeler (1942) found significant differences in behavior between agouti and black rats, but no clear, sharp division between the animals of different coat color. This is to be expected, because temperament is not a single-gene trait but is influenced by many genes.
Cottle and Price (1987)
The rats: Cottle and Price (1987) conducted a more complex experiment comparing the behavior of agouti and black rats. These rats were the descendants of six wild rats trapped in New York. Five generations later, the authors took 12 female and 10 male rats who were heterozygous for agouti (Aa), and bred them to produce agouti (A-) and black rats (aa). These sixth-generation rats therefore had a common genetic background, and were put through behavioral tests.
The behavioral tests and results: In handling tests, the agouti rats were more likely to exhibit defensive behavior and were more difficult to handle than black rats. Specifically, when an experimenter placed a gloved hand on the floor near the rat, a higher percentage of agouti than black rats attacked the hand, and exhibited jumping and running behavior. When the experimenter slowly approached a gloved hand and tried to touch, stroke, then catch the rat, agouti rats were more likely than black rats to attack the hand and were significantly more difficult to touch, stroke and catch.
All black rats could be touched by the second trial, but after five trials 15% of agouti rats had not been touched. All black rats could be stroked by the third trial, but after five trials 32% of agouti rats had not been stroked. The first time a rat was approached with the gloved hand, 76% of black rats could be caught, compared to only 25% of the agoutis. By the fifth trial, all black rats could be caught, compared to 75% of agoutis.
Cottle and Price also found agouti rats to be more active in an open-field test, and groomed slightly less than nonagouti rats when placed on a platform.
CItations
Experimental evidence: Coat color and temperament in rats. (n.d.). Retrieved February 11, 2021, from http://www.ratbehavior.org/ExperimentalCoatTempmt.htm
Grandin, T., & Deesing, M. J. (2014). Genetics and behavior during handling, restraint, and herding. Genetics and the Behavior of Domestic Animals, 115-158. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-394586-0.00004-4





